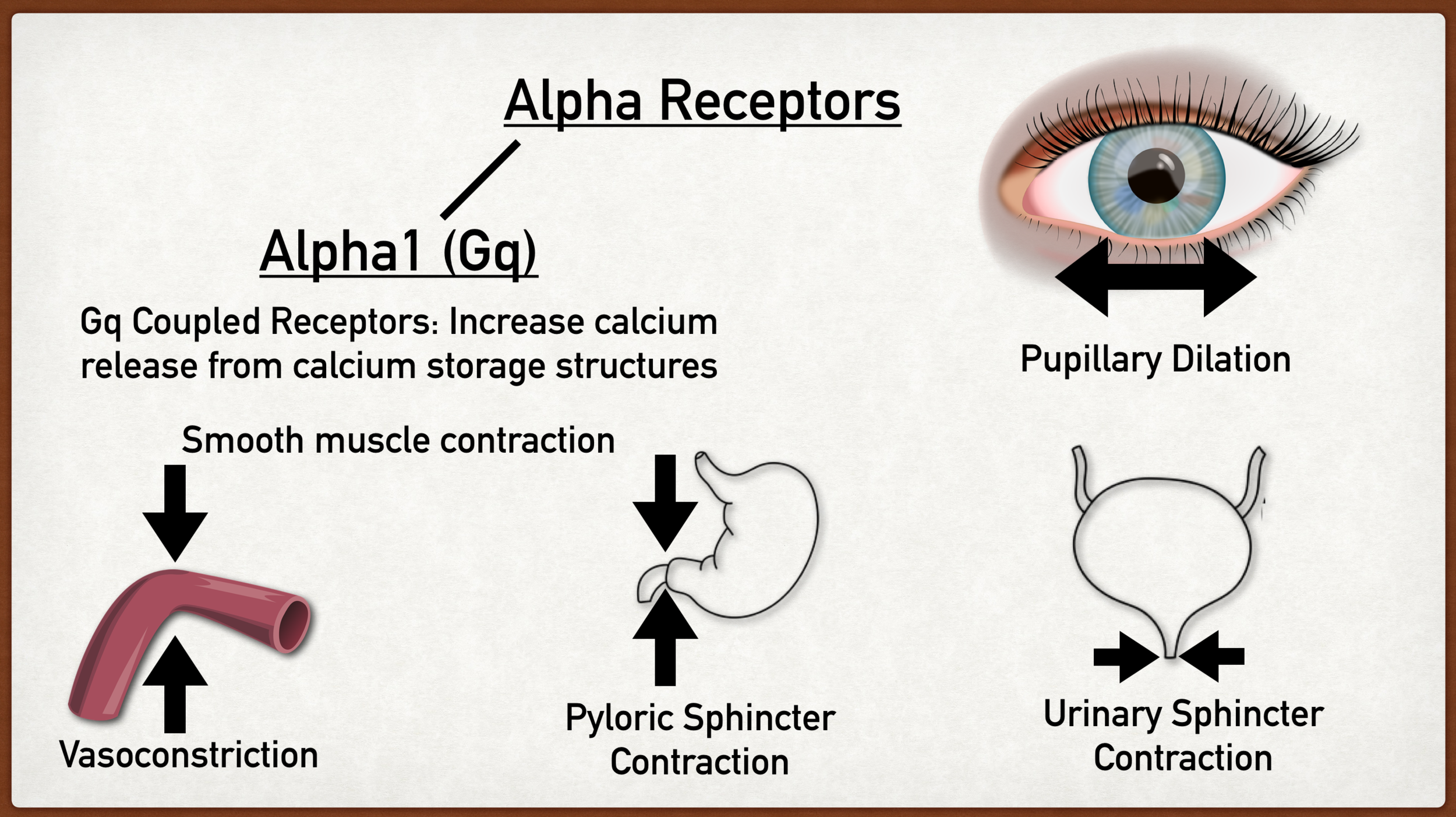
Alpha Adrenergic Receptor Types, Function, Location, and Stimulation Effects Made Easy — EZmed
The α 1-adrenergic receptor (AR) subtypes (α 1a, α 1b, and α 1d) mediate several physiological effects of epinephrineand norepinephrine.Despite several studies in recombinant systems and insightfrom genetically modified mice, our understanding of the physiological relevance and specificity of the α 1-AR subtypes is still limited.Constitutive activity and receptor oligomerization have.
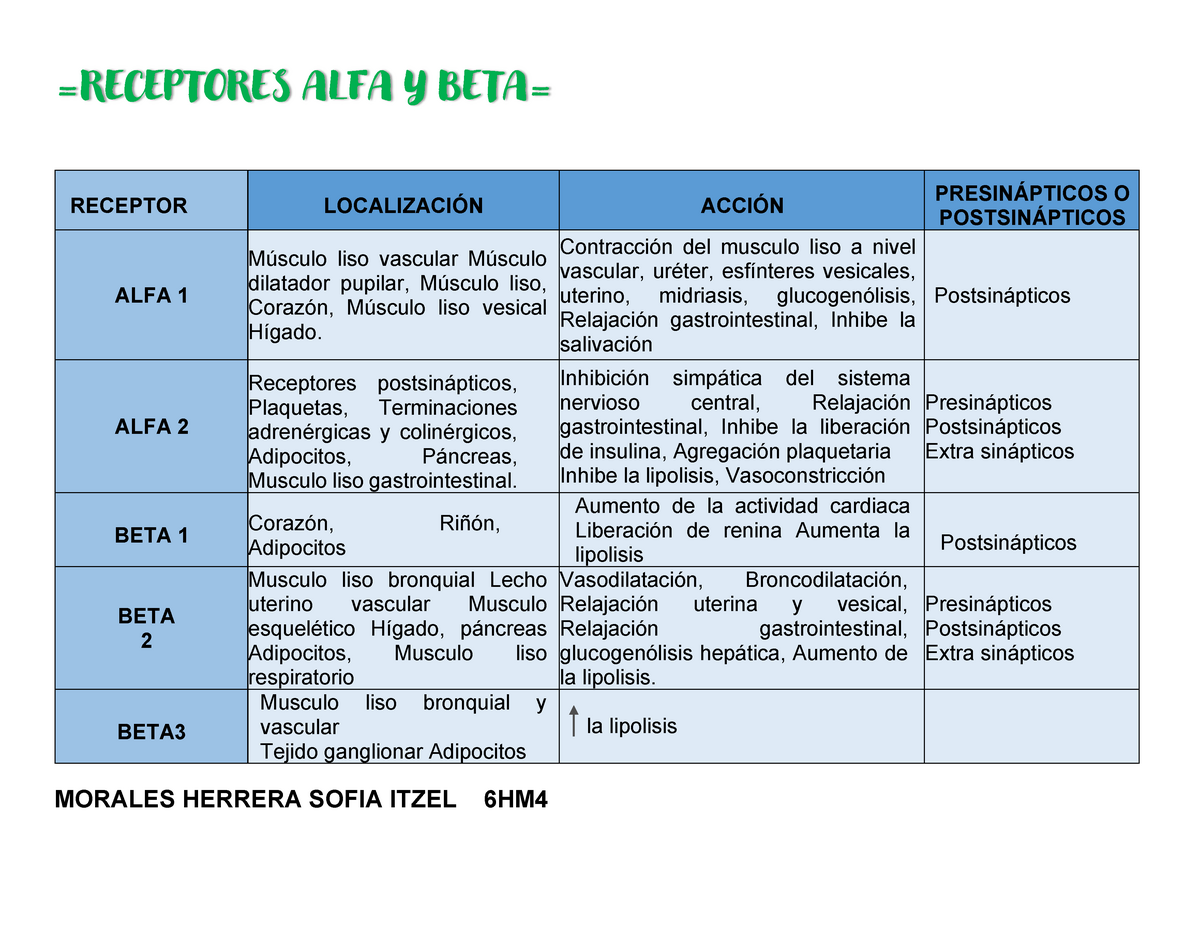
Localización DE LOS Receptores =RECEPTORES ALFA Y BETA= MORALES HERRERA SOFIA ITZEL 6HM
Clinicamente, alguns fármacos apresentam seletividade distinta em relação a estes últimos. Os α 1-receptores têm maior afinidade por fenilefrina do que os receptores α 2, enquanto a clonidina possui maior seletividade aos receptores α 2 e tem menor efeito nos receptores α 1, por exemplo. Os receptores α 1 são ativados por uma.
Receptores adrenérgicos Alfa 1 YouTube
Existen varios tipos de receptores adrenérgicos divididos en dos grupos principales, los receptores alfa (α) y los receptores beta (β). [5] Receptores α: se unen con adrenalina y noradrenalina. Se subdividen en receptor α 1 y el receptor α 2. La fenilefrina es un agonista selectivo del receptor α1.
Alpha Adrenergic Receptor Types, Function, Location, and Stimulation Effects Made Easy — EZmed
Los receptores adrenérgicos son un tipo de receptor en el que se acoplan catecolaminas. Están implicados en varias funciones del sistema nervioso simpático, el cual implica respuestas de lucha y huida. A continuación veremos más a fondo los tipos y subtipos de estos receptores, además de explicar en qué se encuentran implicados cada uno.
Diferencia entre los receptores alfa y beta Definición, mecanismo, función, diferencias

The α 1 -adrenergic receptor (AR) subtypes (α 1a, α 1b, and α 1d) mediate several physiological effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine. Despite several studies in recombinant systems and insight from genetically modified mice, our understanding of the physiological relevance and specificity of the α 1 -AR subtypes is still limited.
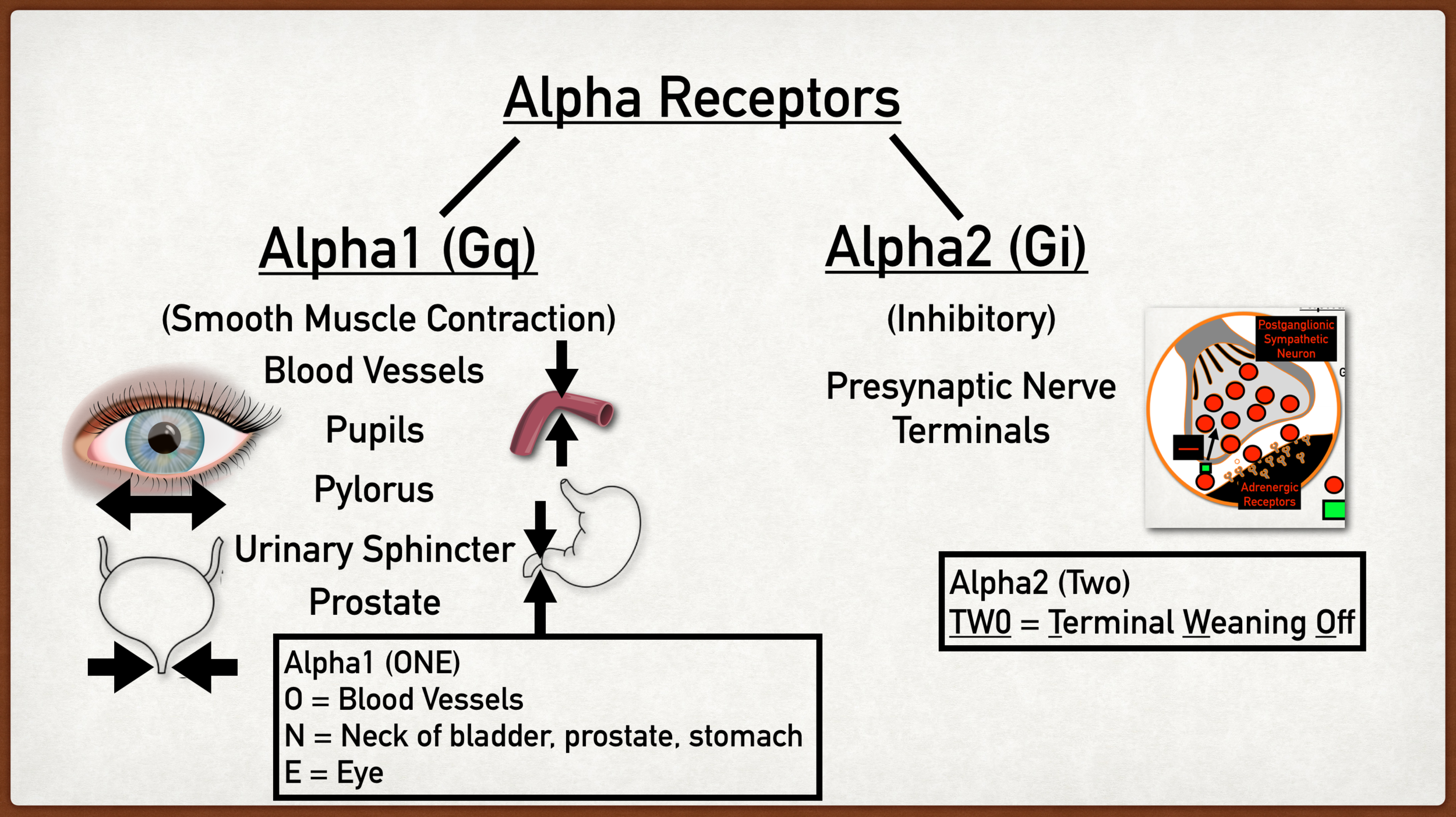
Alpha Adrenergic Receptors Alpha1 & Alpha2 YouTube

Os receptores alfa são subclassificados em duas categorias principais: alfa-1 e alfa-2. Os receptores alfa-1 estão localizados principalmente nos vasos sanguíneos, onde sua ativação leva à vasoconstrição e aumento da pressão sanguínea. Já os receptores alfa-2 estão presentes no sistema nervoso central e estão envolvidos na.
Aula SNA Farmacologia Adrenérgica Simpatomiméticos e Simpatolít…

Abstract. α 1 -Adrenoceptors are seven transmembrane domain GPCRs involved in numerous physiological functions controlled by the endogenous catecholamines, noradrenaline and adrenaline, and targeted by drugs useful in therapeutics. Three separate genes, whose products are named α 1A -, α 1B -, and α 1D - adrenoceptors, encode these receptors.
Neurotransmitter Action GProteinCoupled Receptors Foundations of Neuroscience

a Flow chart of the selection process of conformationally selective nanobodies from the yeast-displayed nanobody library. For rounds 1 and 2, 0.2 μM α 1A AR bound to oxymetazoline (oxy) was used.
Crystal Structure of Human α2C Adrenergic Receptor Reported
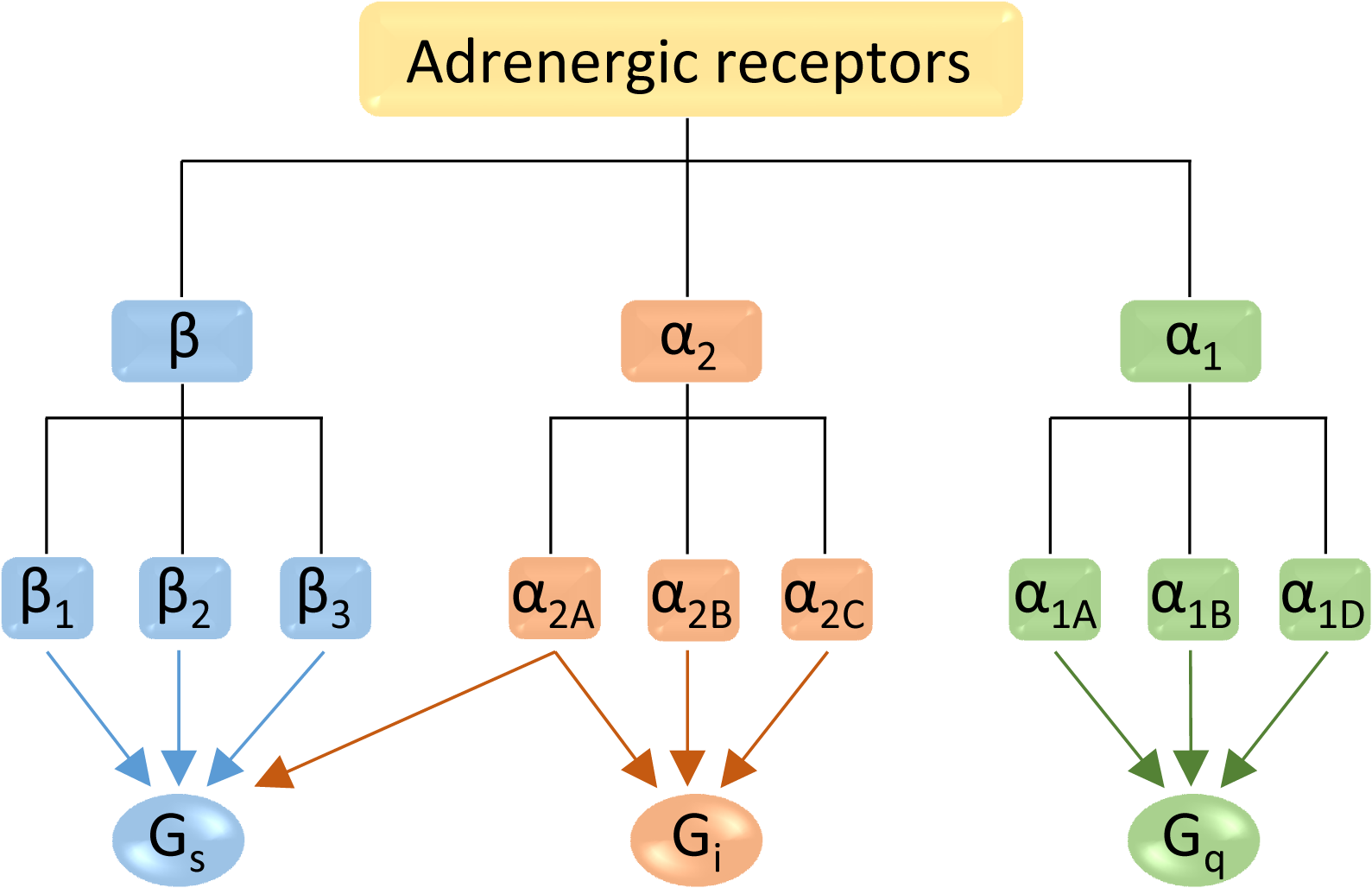
alpha-1 (α 1) adrenergic receptors are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) associated with the G q heterotrimeric G protein. α 1-adrenergic receptors are subdivided into three highly homologous subtypes, i.e., α 1A-, α 1B-, and α 1D-adrenergic receptor subtypes. There is no α 1C receptor. At one time, there was a subtype known as α 1C, but it was found to be identical to the previously.
Physiology of various α2adrenergic receptors. Download Scientific Diagram

The Lerner Research Institute, The Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH, United States; The α 1-adrenergic receptors (ARs) are G-protein coupled receptors that bind the endogenous catecholamines, norepinephrine, and epinephrine.They play a key role in the regulation of the sympathetic nervous system along with β and α 2-AR family members.While all of the adrenergic receptors bind with.
(PPTX) SISTEMA NERVIOSO SIMPÁTICO Receptores alfaReceptores Beta 1 BBB 2 12 3 RECEPTORES

The indication for the use of an alpha-receptor modifying medication depends on which receptor is the target: the alpha-1 receptor or the alpha-2 receptor. Further, when administering a pharmacologic agent, it can exert either agonistic or antagonistic activity on the alpha receptors. This activity reviews the various alpha receptors and examines the types of agents that can act upon these.
Ciencias de Joseleg Receptores adrenérgicos
Abstract. α 1 -adrenergic receptors are G-Protein Coupled Receptors that are involved in neurotransmission and regulate the sympathetic nervous system through binding and activating the neurotransmitter, norepinephrine, and the neurohormone, epinephrine. There are three α 1 -adrenergic receptor subtypes (α 1A, α 1B, α 1D) that are known to.
Agonistas De Receptores Adrenergicos
The alpha-2A receptor was localized in the inner rat retina by immunohistochemistry. Brimonidine reduced the rate of RGC loss in the calibrated rat optic nerve injury model even when dosed 12 and 24 hours before injury, consistent with a long-term enhancement of RGC resistance to stress. Brimonidine was also neuroprotective in the lasered.
Receptores Adrenergicos Alfa 1 Y 2
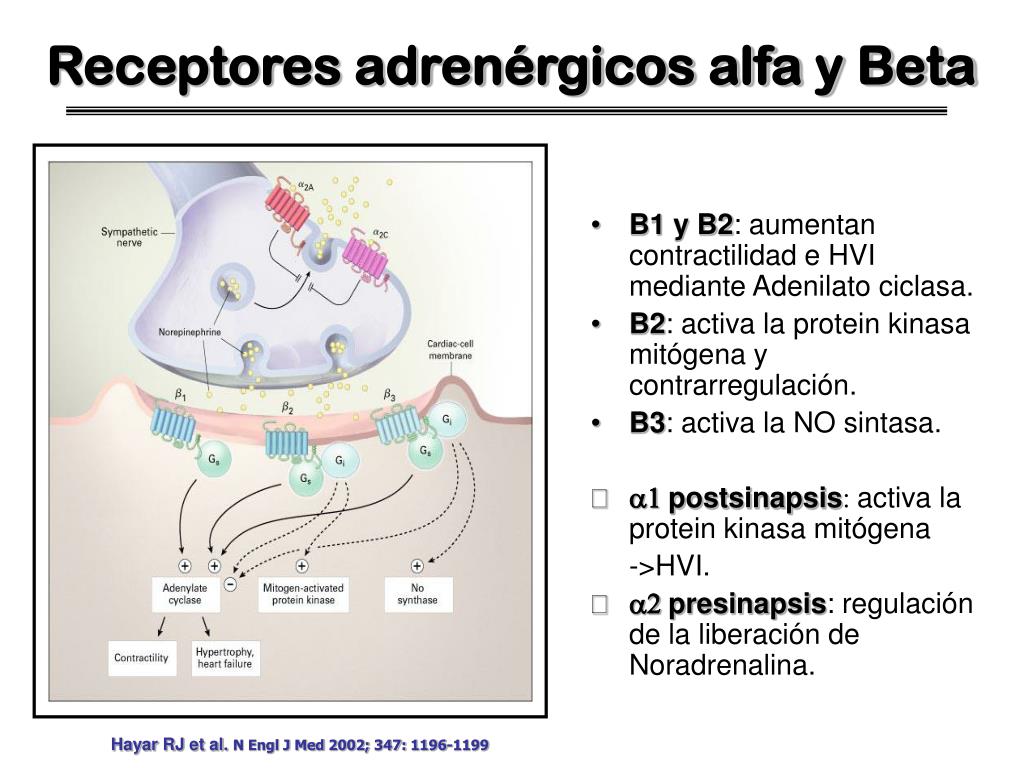
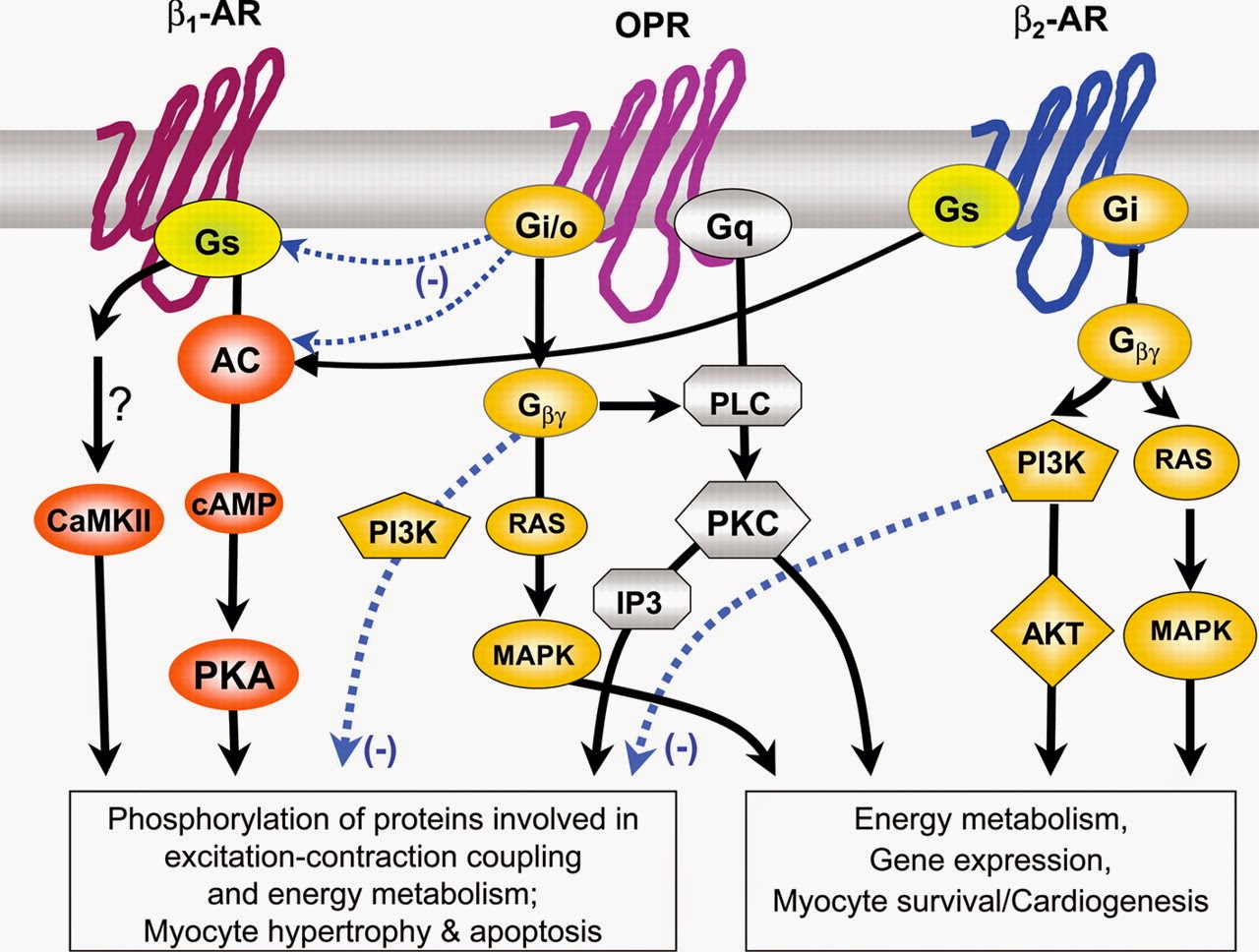
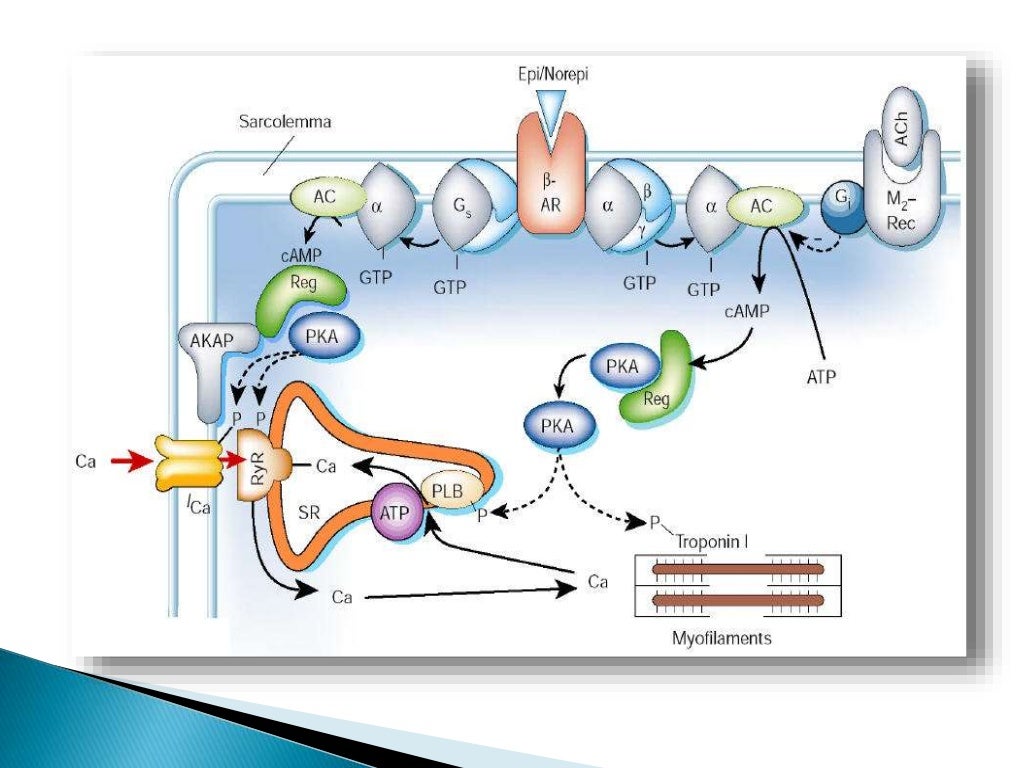
Os mais importantes receptores adrenérgicos são cinco (5): α 1, α 2, ɮ1, ɮ2 e ɮ3. α1- são receptores acoplados à proteína G, agindo via fosfolipase C, aumentando o Ca++ intracelular. Principal responsável pelo tônus da PA. Também distribuído em algumas glândulas. α2- : são receptores acoplados à proteína Gi, inibindo a.
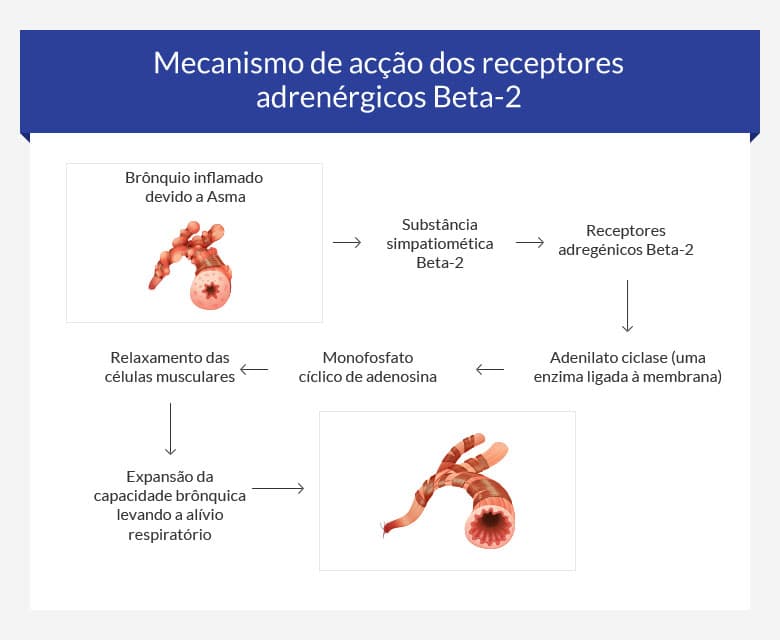
O que são Agonistas dos receptores adrenérgicos Beta2?
α1-Adrenergic receptors (ARs) are members of the G-Protein Coupled Receptor superfamily and with other related receptors (β and α2), they are involved in regulating the sympathetic nervous system through binding and activation by norepinephrine and epinephrine. Traditionally, α1-AR antagonists were first used as anti-hypertensives, as α1-AR activation increases vasoconstriction, but they.
Alpha Adrenergic Receptor Types, Function, Location, and Stimulation Effects Made Easy — EZmed

The alpha-2 ( α2) adrenergic receptor (or adrenoceptor) is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) associated with the G i heterotrimeric G-protein. It consists of three highly homologous subtypes, including α 2A -, α 2B -, and α 2C -adrenergic. Some species other than humans express a fourth α 2D -adrenergic receptor as well. [1]
.

